
Preview in:
Enter reverse image search: a tool often used by journalists and marketers, but surprisingly underutilized in the design world.
Many think it is just a way to track where an image came from. However, it's a strategic asset that can help protect your creative output, uncover higher-res sources, and even find out if your work is being used without permission.
For graphic designers, reverse image search can save hours of research and countless headaches. It's also a subtle SEO ally that supports smarter content handling across websites, portfolios, and digital branding efforts.
This guide will explore how designers can unlock the full benefits of reverse image search (beyond the obvious) and integrate it into their creative workflow.
What is Reverse Image Search?
Reverse image search is the process of submitting an image, rather than a keyword, to a search engine to find visually or contextually similar matches.
Instead of typing a phrase like "modern minimal logo," you upload the image itself, and the search engine returns matching results from around the web.
Most designers are familiar with tools like Google Images and TinEye, but newer AI-powered platforms go further.
Services like Bing Visual Search or Yandex offer layered image analysis, identifying textures, faces, product types, and design styles, even when those aren’t exact duplicates.
These tools work by scanning the image’s unique features (edges, shapes, color composition, and metadata) and comparing them against indexed visuals across the internet.
They can also match against partially cropped or watermarked content, making it useful for tracking down reused assets or discovering derivative work.
For graphic designers, this opens up use cases well beyond the average image search.
Whether you’re-
- Validating a concept
- Verifying the source of client-provided materials or,
- Simply trying to explore similar design directions
-reverse image search can serve as a visual research engine tailored to your style.
It’s a far more intelligent way to handle reference material, and increasingly essential as visual content continues to dominate digital branding.
Verifying Originality and Avoiding Copyright Issues
Designers are constantly sourcing and interpreting visual elements, whether from clients, stock libraries, or their own inspiration boards. But in a world overflowing with recycled content, verifying image originality is more important than ever.
Reverse image search helps you determine whether a visual asset has been used before, and if so, where and how.
If a client sends you a logo, illustration, or “inspiration photo,” you can run it through a tool like Google Images or Lenso AI to see if it's been copied or downloaded from somewhere else.
This is especially critical when designing identities, packaging, or ads that may face legal scrutiny.
Even for creatives working with stock imagery, it's worth checking how often that image has been used online. Overused visuals can dilute a brand’s identity or cause unintentional overlaps with competitors.
On the flip side, reverse search also helps protect your original work. Upload your designs to see if they’ve been reposted, repurposed, or even sold without your consent. This is particularly useful when publishing your work on social platforms or online portfolios.
And if you're about to create a website or launch a new page with heavy visual content, this step acts as a final QA check. It ensures the images you use are not unknowingly plagiarized or widely circulated in a way that diminishes your brand.
Reverse image search can preserve creative credibility.
Finding Higher-Quality Versions of an Image
Clients often send images pulled from Google, social media, or outdated archives, usually compressed, low-resolution, or watermarked. For a graphic designer, working with subpar images isn’t just frustrating; it can compromise the final output’s quality.
Reverse image search offers a direct way to locate the highest-quality available version of any image. By uploading a low-res file, you can scan across multiple platforms for sharper, original sources. It can save time you’d otherwise spend redrawing, enhancing, or hunting through stock libraries.
It’s particularly useful when clients don’t know where they sourced the image or when the original creators aren’t credited. Instead of guessing, reverse search gives you direct leads.
Key ways designers use this feature:
- Locating Original Stock Images: Helps track down the clean, unwatermarked version of an image on stock platforms like Shutterstock or Adobe Stock.
- Finding Press-Quality Images: Reverse search often leads to media kits or official releases containing high-res visuals suitable for publication.
- Sourcing Artist Portfolios: Directs you to the creator’s website or online portfolio, making it easier to request permissions or purchase usage rights.
- Replacing Low-Res Client Assets: Provides options to swap out blurry, stretched, or compressed visuals with professional-grade alternatives.
For any designer aiming for quality and professionalism, this tool bridges the gap between rough drafts and polished results.
Tracking Where Your Designs Appear Online
Once your work goes live, it’s nearly impossible to track where it ends up manually. Whether you're publishing client assets, social media graphics, or branding materials, reverse image search can help monitor where your visuals are being used online.
By uploading your own designs periodically, you can find unauthorized usage, reposts without credit, or websites that are profiting off your work. This isn’t just a copyright concern. It’s also a brand integrity issue.
Clients may not want their custom designs appearing in unrelated contexts, especially without consent.
Reverse search can also validate whether your assets are being shared as intended. For freelancers or studios working under white-label contracts, it gives insight into how and where the final designs are being distributed.
This process mirrors what an AI SEO agency might do at scale. By automating image tracking, agencies can assess-
- Visual SEO performance
- Brand visibility across platforms and
- How image content contributes to rankings or referral traffic
Designers can adopt a similar mindset to evaluate ROI on visual campaigns.
It’s about having visibility and leverage when needed. Whether for protecting your IP or understanding reach, reverse image search is one of the few tools that turns visual content into measurable data.
Gathering Visual Inspiration and Competitor Analysis
Creative block is inevitable, but reverse image search offers a smart way to gather fresh ideas, without scrolling aimlessly through Instagram or Pinterest. Instead of keywords, you feed the algorithm a reference image and let it show you stylistic matches, layouts, or design variations.
This is particularly helpful when working within a specific design aesthetic or trying to meet a client’s vague creative brief.
Uploading a single image can surface dozens of related compositions, color schemes, or font treatments from across the web, sometimes from regions or industries you wouldn’t have considered otherwise.
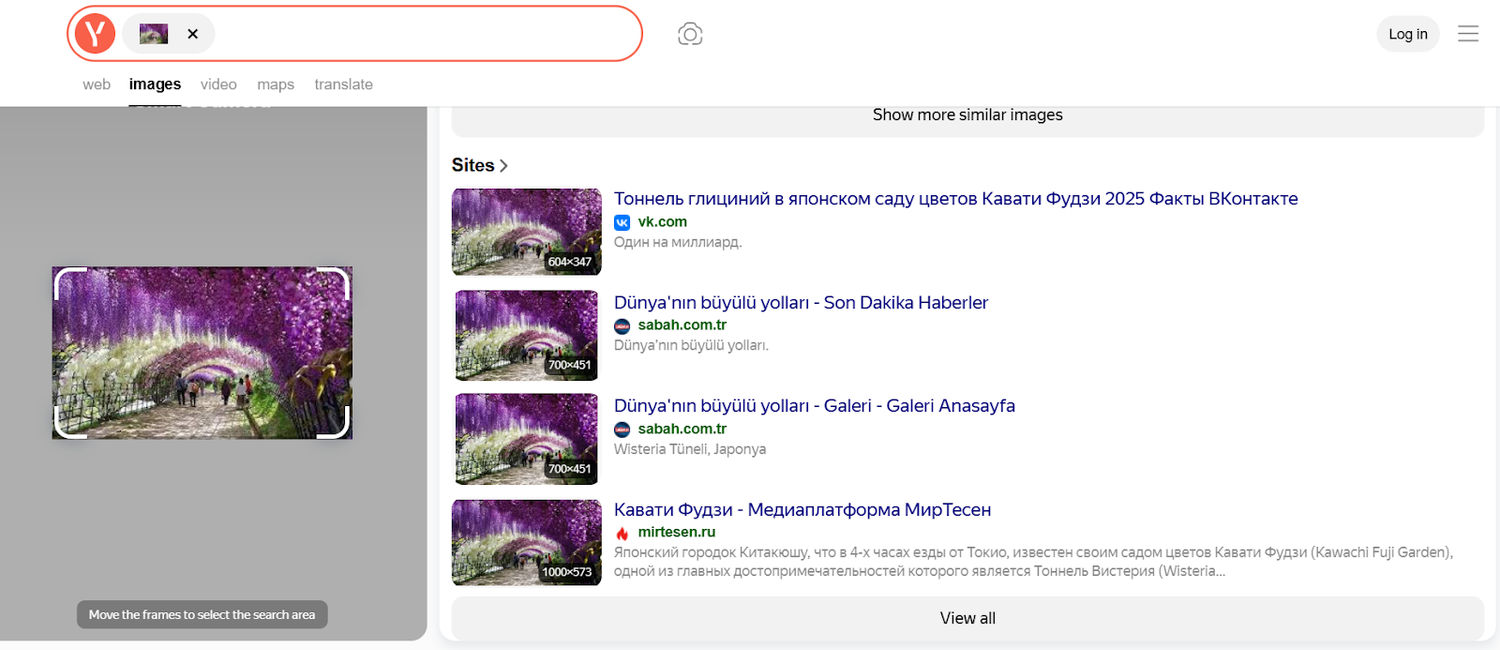
It’s also an underrated tool for light competitor analysis. If a client references a specific company’s branding, you can reverse-search elements like their logo design, banner ads, or print materials.
It can allow you to explore how their brand is represented across platforms and spot design patterns you may want to refine or avoid.
Plus, it's useful when you're sourcing ideas for pitch decks or moodboards. Rather than assembling assets piece by piece, reverse image search offers a design-adjacent cluster of concepts in one step.
For designers who want to keep their work original but aligned with current trends, reverse image search becomes part of a faster, more intentional inspiration process.
Enhancing SEO for Image-Based Content
For graphic designers who regularly publish visual content, SEO isn’t just about text. Images contribute to search rankings, brand visibility, and traffic, especially on platforms like Google Images, Pinterest, and visual search engines.
Reverse image search plays a subtle but effective role in this process.
Before uploading visuals to a website or portfolio, designers can use reverse image search to ensure originality and optimize their image SEO strategy. It’s a proactive way to check if the image is already indexed elsewhere or used by competitors.
Here’s how reverse image search supports image SEO efforts:
- Preventing Duplicate Content Issues: Helps confirm whether an image is unique or overly used, reducing the risk of duplicate content flags in image search rankings.
- Identifying Image Attribution Opportunities: Reveals where your images appear, giving you a chance to request backlinks or proper credits, both of which contribute to SEO authority.
- Optimizing for Search Intent: Enables you to check how similar images are described and tagged, refining your own alt text, filenames, and metadata for better alignment with search queries.
- Supporting Backlink Strategies: By discovering unauthorized uses, you can negotiate credits or links, a tactic often used by SEO professionals and agencies.
Image SEO often gets overlooked, but it’s a low-effort, high-impact way to increase your brand’s organic reach, especially in creative industries.
Conclusion
Reverse image search offers graphic designers far more than just curiosity value. From protecting your creative assets to uncovering inspiration, verifying originality, and enhancing SEO, it’s a multipurpose tool that fits seamlessly into a designer’s workflow.
In a digital landscape where visuals drive both engagement and discoverability, leveraging reverse image search is a smart, proactive habit.
Whether you work solo, in a studio, or collaborate with an AI SEO agency, mastering this tool can amplify both your creative output and your business impact.
Continue reading

News
Research Mode & Advanced Filters | Lenso.ai for Professionals
There’s been a huge update to Research Mode on lenso.ai! If you are considering the purchase of the Professional subscription, keep reading. We will explain what Advanced Filters are and how they’re helpful in finding only the most accurate matches in the Research Mode.

News
Artificial Intelligence's role in photography in 2026
This article explains how reverse image search AI changes the photography industry, its implications for photographers nowadays, and what ethical matters stem from those technological innovations.

News
Categories on lenso.ai | People, Duplicates, Places and more
When you visit lenso.ai for the first time, finding the right results might seem like a challenge. In reality, it’s easy! All you have to do is pick the right category for your search. In this article, we will explain how you can find categories and which category is the best for your use case.

News
Best Reverse Image Search Tools in 2026 - Categorized
Ever needed to find a specific detail in an image? Maybe it's a rare plant in the background, a book someone's holding, or even your own face in a crowd. The tool you choose for this task makes all the difference. In this article, we'll explore the different categories of image details you might search for and explain why selecting the right tool is crucial for finding the exact image you need.
![Best Chrome Extensions for Reverse Image Search [2026 Ranking]](https://img.lenso.ai/blog/best-chrome-extensions/best-chrome-extensions?updatedAt=1749627943559&tr=w-768,h-auto)
News
Best Chrome Extensions for Reverse Image Search [2026 Ranking]
Chrome extensions make everyday web usage even easier. You're probably already using an ad blocker, SEO tools, or other productivity extensions. Now is the perfect time to add a reverse image search tool to that list. Check out the best Chrome extensions for reverse image search!
